Ensuring our activities online are safe and private is the need of the hour. We need to ensure that websites are secure and safe to visit. But at times, it gets confusing to do so, and non-secure sites with malicious intentions are quite deceiving and trick the user into believing that it is safe. Awareness and information regarding the safety and security of websites are pretty important. And in this article, we’ve answered most of the common queries and questions regarding what is Site Not Secure, what it means, and why it is important.
Related | 4 Ways To Open Non-Secure Websites In Google Chrome
Everything You Need to Know About “Site Not Secure” Error
Below we have covered all questions about the Site not secure error, including what it is, its importance, and how to avoid it or turn it off or access websites showing the error. Keep reading.
1. What Does It Mean When a Site Is Not Secure?
There are many reasons why a site is not secure, mainly because they have expired certificates or lack encryption. These websites are not safe enough for the user to visit and access, as you are putting your privacy and safety at risk. As we store a lot of personal information on web browsers – passwords, addresses and payment information, etc. are all at risk.’
2. How Do I Know if a Website Is Not Secure?
Web browser developers put in a lot of effort to provide users with a number of warnings when a site is not secure. These warnings usually occupy the entire screen so that it is impossible for them to go unnoticed. Apart from these warnings, here’s how to check is a website is secure or not:
- If you are on a popular/known website, ensure the URL is correct and does not have any typographical errors.
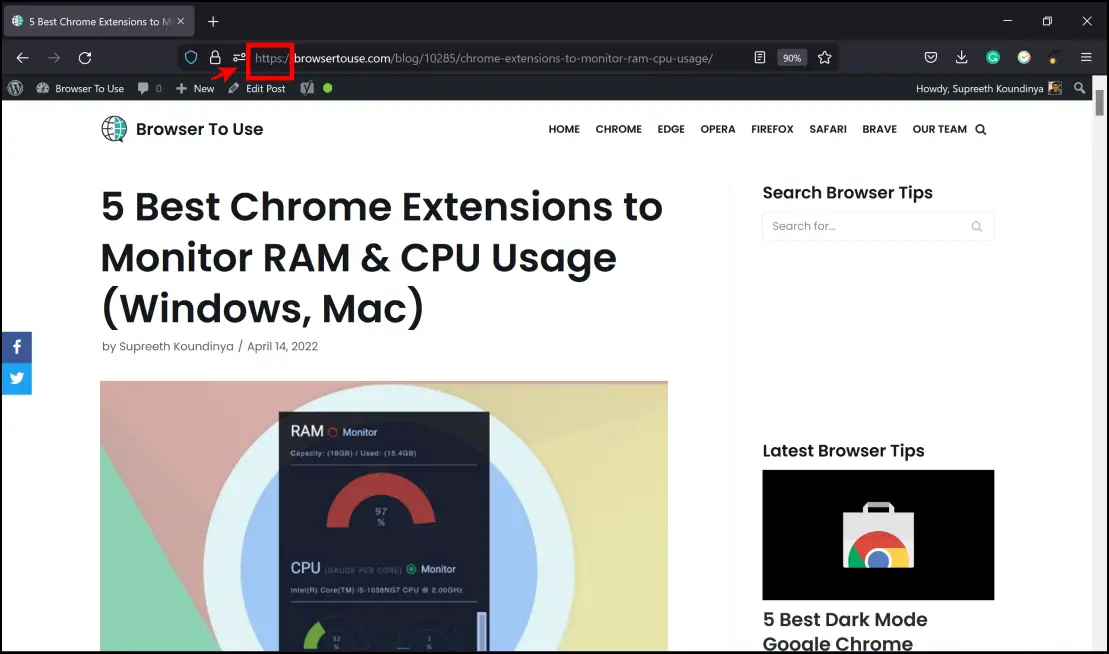
- Ensure that the website is operating on an HTTPS protocol.
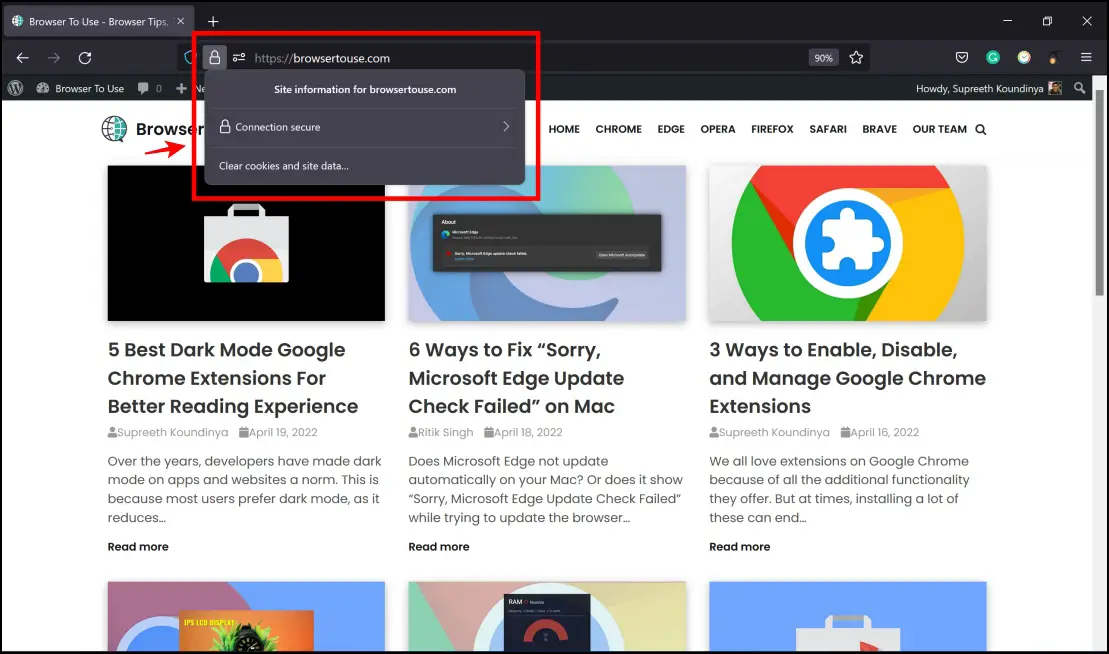
- Ensure the certificates on the websites are up to date – you can do this by clicking on the padlock icon on the toolbar of your web browser.
- Be wary of trusting any claims of safety made by these websites through stamps and seals.
- Observe the website’s UI. Most websites that are constantly updated and well maintained come with a good and modernized user interface.
3. How Dangerous Is It to Visit Non-secure Websites?
Malicious websites track a lot of your data and usually have a lot of notorious intentions. Your payment information, addresses, and passwords are at risk of being breached and misused. Non-secure sites are usually not encrypted. This means that once you enter your data on a non-secure site, someone else can easily capture this data while pretending to be you.
While in no way are we implying that every single non-secure website does the same, for the sake of ensuring privacy, we advise you to treat all of these sites as potentially dangerous ones – especially if they ask you to enter personal information.
4. Can You Still Visit Non-secure Websites?
The answer from our end is a big no. Unless you are truly aware of what website you are visiting, and you do trust the site owner and are completely aware of what you are getting into, you can proceed to visit non-secure sites at your own risk. Here are different methods to open non-secure websites in Chrome and other browsers.
5. What Is HTTPS and How Is It Different From HTTP?
In the modern-day internet era, HTTPS is the most widely used protocol for browsing the web, owing to the extra security due to encryption. It is a good idea to encrypt transferred data. It means that information sent between your browser and the website is not accessible to third parties such as ISPs, network administrators, and intruders. It allows you to enter passwords or credit card information without fear of malicious elements online.
HTTP (Hypertext transfer protocol) is a protocol used to fetch documents over the internet, and it facilitates any data exchange on the internet. It is a non-encrypted connection which is fine for basic activities or visiting public websites that don’t require you to send any login information to it.
On the other hand, HTTPS is an encrypted connection that encrypts sensitive data you upload online such as username and password. It prevents people from eavesdropping on the same. The difference between these two protocols is that an SSL or a TLS certificate is added to the HTTPS protocol. Simply put, these certificates are lines of code on web servers that provide an additional layer of security.
6. How Does HTTPS work?
HTTPS is a protocol that offers encryption to any websites you visit. Using HTTPS means that a foundational layer of security is ensured. Let us quickly understand what HTTPS does :
- HTTPS ensures authenticity. This means that the server running the website is legitimate and genuine and all the identity it claims is verified and true.
- HTTPS ensures integrity in internet communication. This means that whatever message exchange or communication that happens between you and the server of the website is untampered and unaltered, and nobody can make any changes to the same.
- HTTPS ensures secrecy, meaning that nobody can read what your communication messages contain, and this information remains just between you can the web servers.
But HTTPS does not ensure 100% security at all times due to the following reasons:
- Cryptography cannot always be perfect, as with enough money and time to spend, an entity can attempt to decrypt your messages.
- If we were to understand how authenticity works, it is a ‘chain’ of trust. For each step in the certification chain, a trusted entity verifies them and then the next one, and so on. It means that if you trust one link in the chain, you end up trusting all the other links. So, if any one link in the chain is broken or compromised, the root authority in the chain can be tricked into verifying an invalid certificate.
- HTTPS does not protect the whole, but just a part of it. This means there is a slight potential for your data to be breached even before it gets encrypted, probably when malicious entities try to grab your data through keyloggers or local storage.
7. How Do I enable HTTPS on all sites?
Across popular browsers, it is easy to enable HTTPS always be on through various methods.
- Through built-in options: Google Chrome, Firefox, and Brave Browser come with a built-in feature to enable HTTPS.
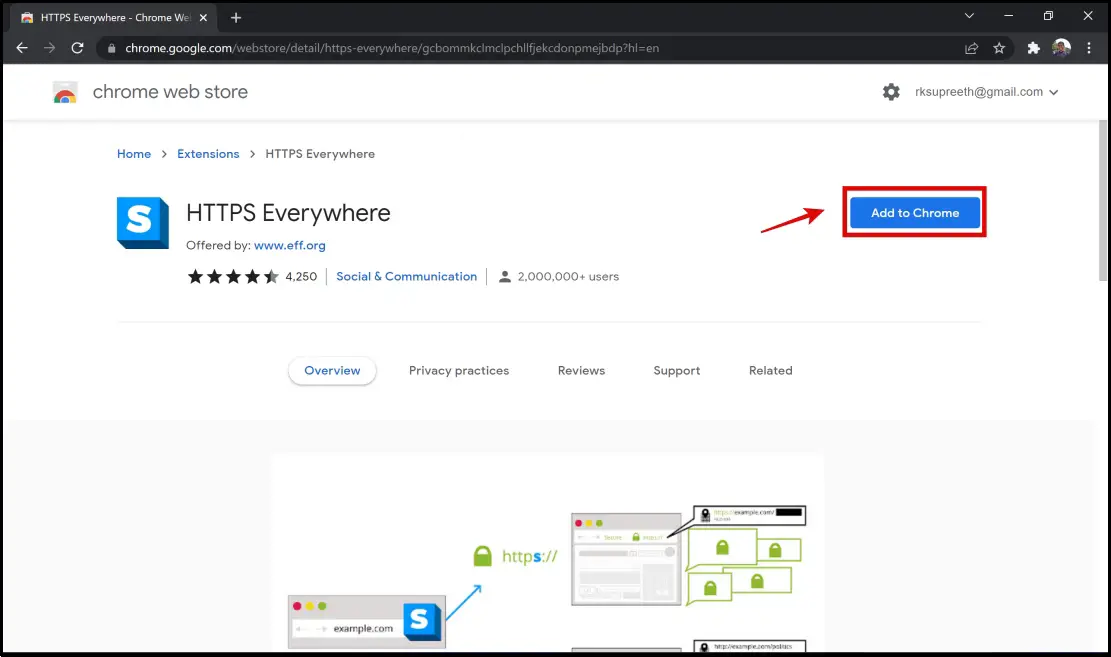
- HTTPS Everywhere: HTTPS Everywhere is a minimal and popular extension that can be used to enable your browser to use HTTPS all the time. This extension is available for Google Chrome, Firefox, and Opera Web browser. It is quite stable and easy to use and even offers features to disable HTTPS on certain sites, provided you have a reason to do so.
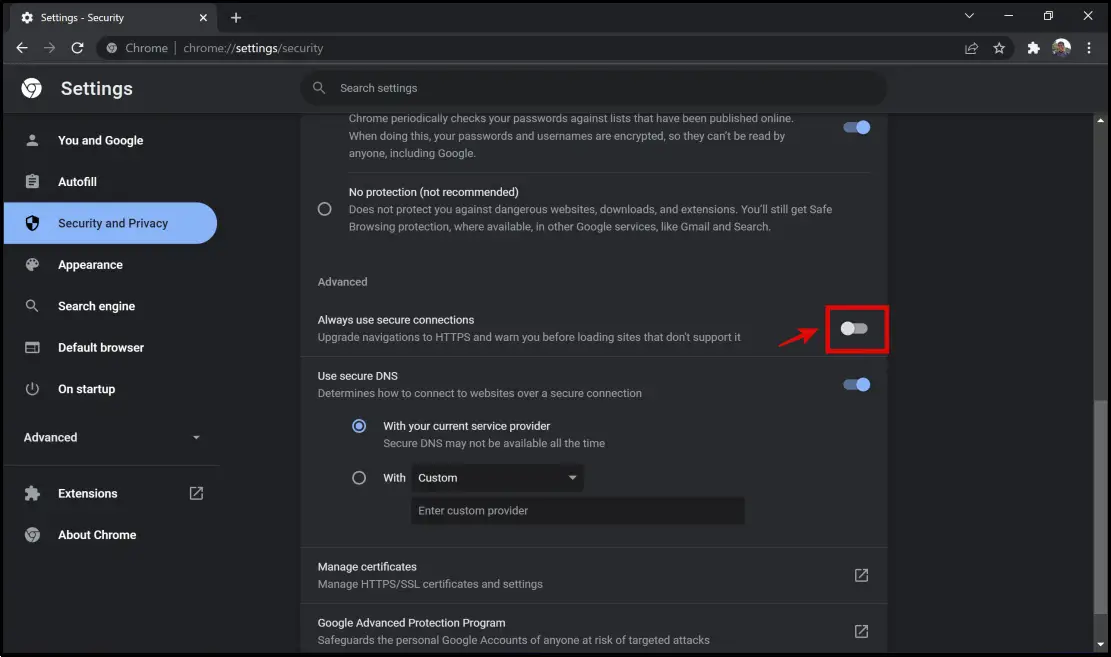
Here’s how to enable or disable always-use HTTPS on your browsers.
8. Is HTTPS Safe? Can I Still Visit Sites With “Site Not Secure” Warning With HTTPS On?
It is neither fully safe nor unsafe to visit a website with HTTPS – let me explain. HTTPS protects the communication between client and server, and in no way does it secure the website itself. It does not protects against malicious elements or protect you from being served malicious content.
HTTPS also does very little to protect you from attacks, but there are many other anti-malware services that your PC is equipped with which prevent the attack. Of course, there is an increased risk when no HTTPS is used or if HTTPS warnings need to be skipped. The lack of HTTPS just makes the attacker’s job slightly easier when it comes to tapping the communication between you and the server.
If there is an error when it comes to validating a certificate, it points to an inability of the site administrator and the hosting providers to set up HTTPS in the right way. This is usually the consequence of the problem of not being able to secure the site or not caring about user security in the first place.
More importantly, we need to be aware that expired certificates indicate that sites are no longer maintained and there is no concern for security at all. So what we need to do is avoid visiting such websites in the first place.
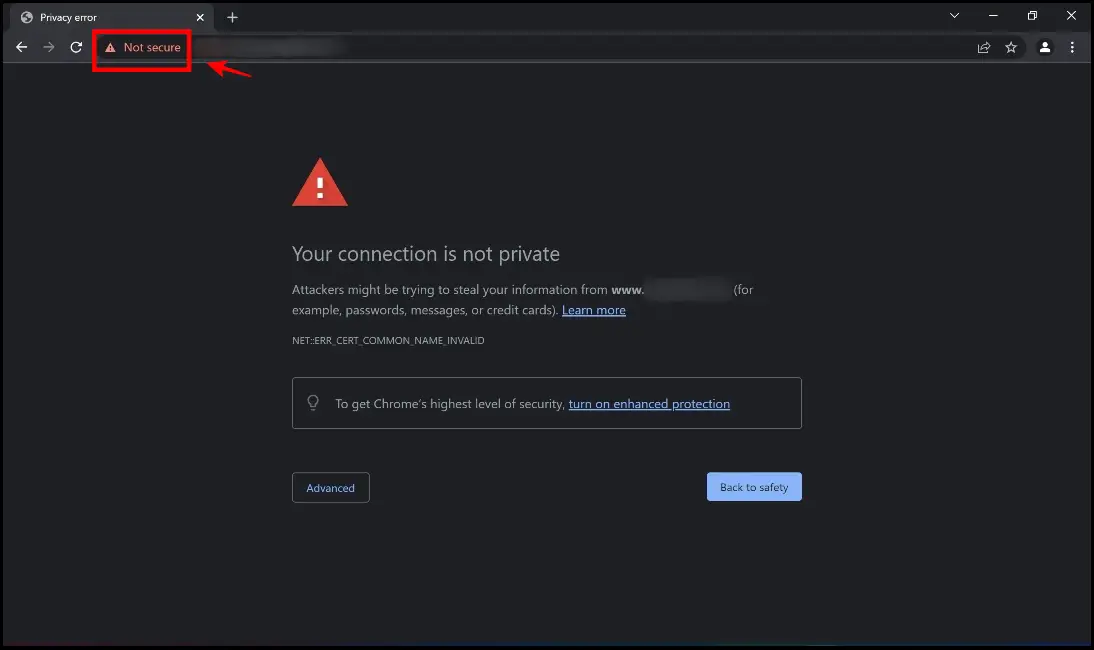
9. What Is Your Connection Is Not Private?
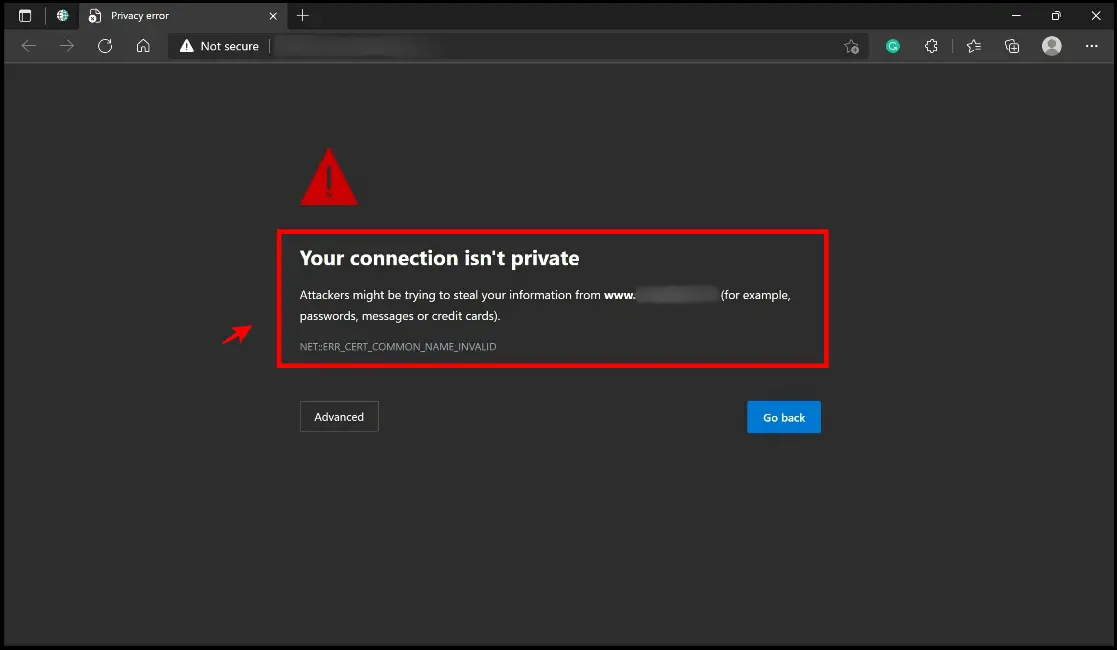
When your browser fails to authenticate a safe connection between the website and your device, an error message saying “Your connection is not private” is shown. It means your browser cannot verify whether a website is safe to visit. The error can occur in any browser. Your web browser checks the website’s security certificate to ensure your privacy and data safety. If a certificate isn’t up to par, your personal information may be vulnerable to online attacks.
In a nutshell, the error “your connection is not private” signifies that: Your connection isn’t secure, and the mistake shouldn’t be overlooked.
10. Is It Safe to Proceed to Websites That Show Connection Is Not Private Error?
There are multiple ways to fix this error, and once you do so, you can safely visit the website. But, in case you want to bypass the warning and visit the site, we would not recommend you do so as it is not a safe practice. Unless you truly trust the owner of the website and are aware of the details of the website, then you may proceed with caution and at your own risk.
11. Why Does This Error Occur and How Do I Fix Your Connection Is Not Private Error?
- Restart Your WiFi Router: A simple solution that is worth trying out is attempting to restart your WiFi router to fix the “Your connection is not private” error. Restarting your WiFi router is a quick way to refresh it and possibly fix the error.
- Temporarily Disable Your VPN: A VPN (Virtual Private Network) encrypts and redirects your internet connection through a distant web server, masking your IP address, increasing your online anonymity, and safeguarding your personal information. Unfortunately, these additional security layers might lead SSL certificates to be blocked, resulting in the message “Your connection is not private.” Disabling your VPN for a short period may eliminate barriers between you and the website, allowing you to determine if your VPN is the source of the issue.
- Switch to Private Network: The common cause of this problem is when users connect to a public network such as a restaurant or airport WiFi. HTTPS is now required for all websites, especially those that gather personal information. Unfortunately, most public networks use HTTP rather than HTTPS. When you conduct transactions over a public network, the information you enter is not as secure, and anyone on the same WiFi network who knows what they’re doing will be able to steal your personal information. As a result, your browser will display the notice “Your connection is not private” as a warning. Instead of utilizing public WiFi, consider accessing the website using a private network such as your home WiFi network or your mobile data.
- Check Date and Time on PC: The “Your Connection is Not Private” error can occur if your date and time on your PC are misconfigured or incorrect.
These are some of the common reasons why this error can occur. Here’s our detailed guide to fixing the Connection is Not Private error in Chrome, Edge, and Firefox.
12. What is an SSL Certificate & How Does It Ensure Websites Are Secure?

An SSL certificate is a type of secure authentication/recognition in the form of lines of code. It distinguishes between webpages, domains, and devices via a thumbprint. It also safeguards the flow of traffic between those objects. If your site requires a login, SSL is required to protect usernames and passwords. If you use forms that ask for sensitive client information, you’ll need SSL certificates to prevent hackers from stealing your data.
13. How is SSL different from TLS Certificates?
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is an Internet technology that provides an encrypted connection between two computers. It confirms the server’s identity and protects data from intercepting by hackers. To put it another way, HTTPS is HTTP with an overlay of TSL certificates. TLS is an upgraded version of SSL, and it contains added protocols to reduce the vulnerability of your encrypted information online.
14. Does HTTPS Use SSL or TLS Certificates?
Most websites that use HTTPS protocol use the TLS certificates as it is an upgraded form of SSL Certificates.
15. How Do These Certificates Ensure a Safe Information Exchange?
A secure connection is established between the user and the server through a secure handshake. It forms the encryption from the interaction of public and private certificate keys. The information exchange or the handshake usually takes place in two steps :
- The first step is the handshake that comes from the browser via the client as it accepts the TLS certificate and states its version.
- In the second step, the server states the encryption version that is used and ensures that the rest of the interaction is safe and based on the provided TLS certificate.
16. In Conclusion, What Are Some of the Best Practices to Ensure Sites Are Secure?
In brief, here are some of the methods by which you can ensure that the websites you visit are secure to use:
- Ensure that you always operate over the HTTPS protocol.
- Remember to see whether all of your websites have the “green color” padlock on the toolbar of your web browser.
- Please refrain from using public networks as it makes you easily vulnerable.
- You can always perform a little background check, mainly through online forums, regarding the site’s legitimacy.
- Ensure you know some or at least little information regarding the website’s ownership and origins if you suspect anything fishy.
- User interfaces that look quite old are huge red flags, and, in most cases, it means that the website has not been updated in a long time.
- Be vigilant regarding all the warnings that your web browser provides. Web browsers these days are built keeping privacy and security in mind, and it mostly never fails to provide you a warning if something goes wrong.
- Do not take risks while visiting non-secure websites if you do not have a clear picture of what the website is.
- Ensure to use secure web browsers and refrain from using experimental versions of web browsers or those that are not renowned.
Wrapping Up
We hope we addressed all of your queries regarding sites not being secure, and we hope you understand what it means to ensure websites are secure. Stay tuned for more such articles and FAQs regarding web browsers, and we’re sure you’ll learn more than a thing or two as you read them!